Industry knowledge
The difference of PVC Plain Film and PET Base Film
PVC plain film and PET base film are two different types of films with distinct properties and characteristics. Here are the main differences between PVC plain film and PET base film:
Material Composition: PVC (polyvinyl chloride) plain film is made from PVC resin, plasticizers, stabilizers, and other additives. It is a type of thermoplastic material that is known for its flexibility and versatility. PET (polyethylene terephthalate) base film, on the other hand, is made from PET polymer, which is a strong and rigid thermoplastic material.
Transparency: PVC plain film is generally more transparent than PET base film. PVC has good optical clarity, allowing for clear visibility of objects or images placed underneath. PET base film, while still transparent, may have a slight inherent haze or tint compared to PVC.
Mechanical Strength: PET base film is known for its superior mechanical strength compared to PVC plain film. PET has high tensile strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability, making it more resistant to tearing, puncturing, and deformation. PVC, although flexible, is relatively less mechanically strong and may be more prone to damage.
Chemical Resistance: PET base film exhibits better chemical resistance compared to PVC plain film. PET is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, solvents, oils, and greases. PVC, while offering some chemical resistance, may be more susceptible to certain chemicals and can degrade or react in the presence of certain substances.
Thermal Stability: PVC plain film has relatively good thermal stability, with a relatively low melting point compared to PET base film. PVC can be easily processed and molded using heat, allowing for various fabrication methods. PET, on the other hand, has a higher melting point and exhibits better resistance to heat and thermal deformation.
Applications: PVC plain film is commonly used in applications such as packaging, laminating, printing, stationery, signage, and construction materials. It is frequently utilized for products like clear bags, flexible packaging, shrink film, and vinyl sheets. PET base film finds application in industries like electronics, electrical insulation, display screens, labels, solar panels, and packaging where mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and chemical resistance are important.
The Classification of PVC Plain Film
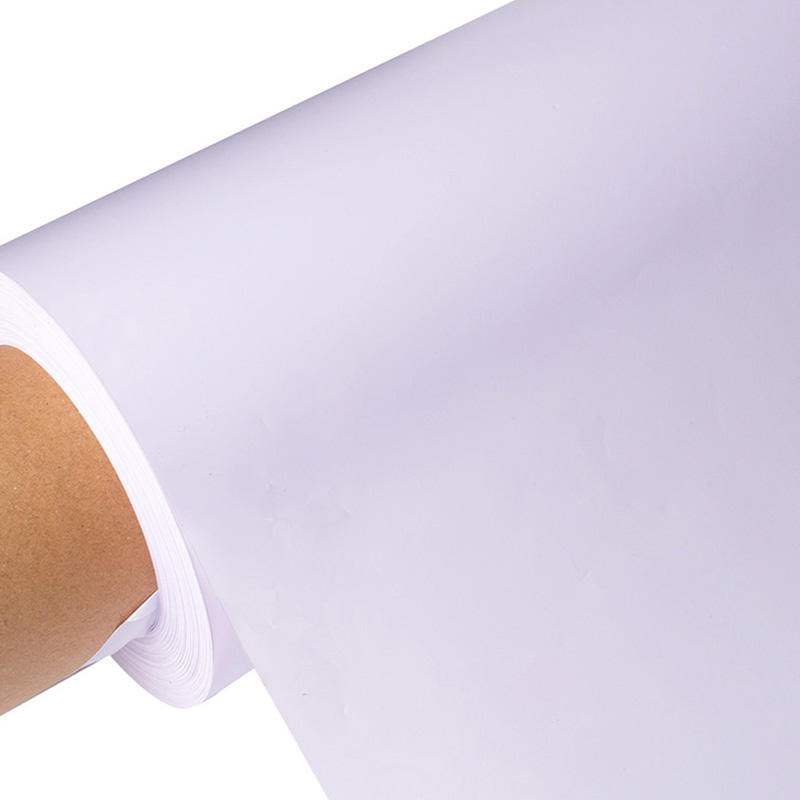
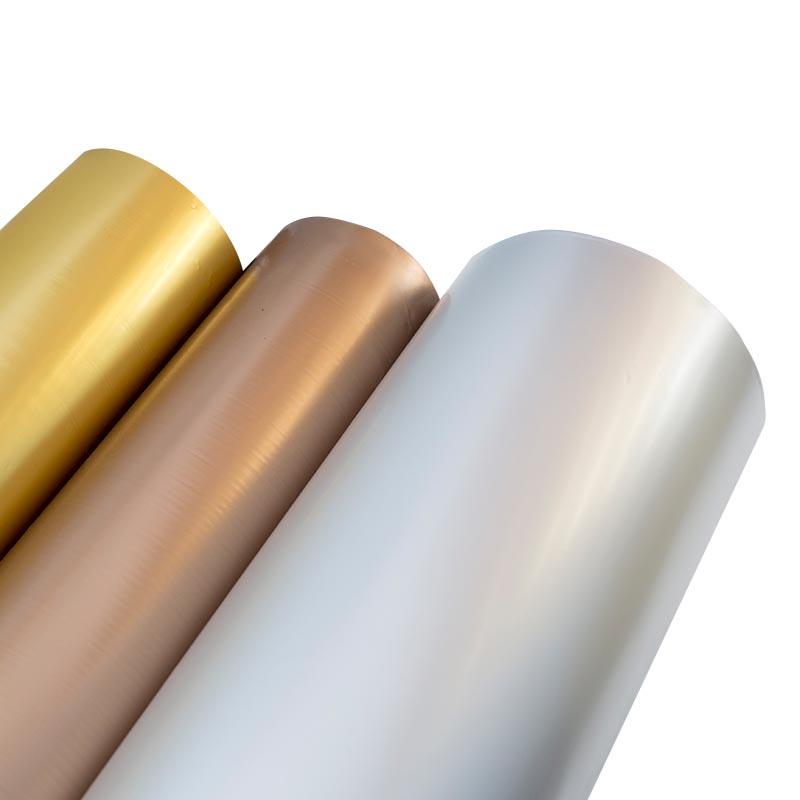
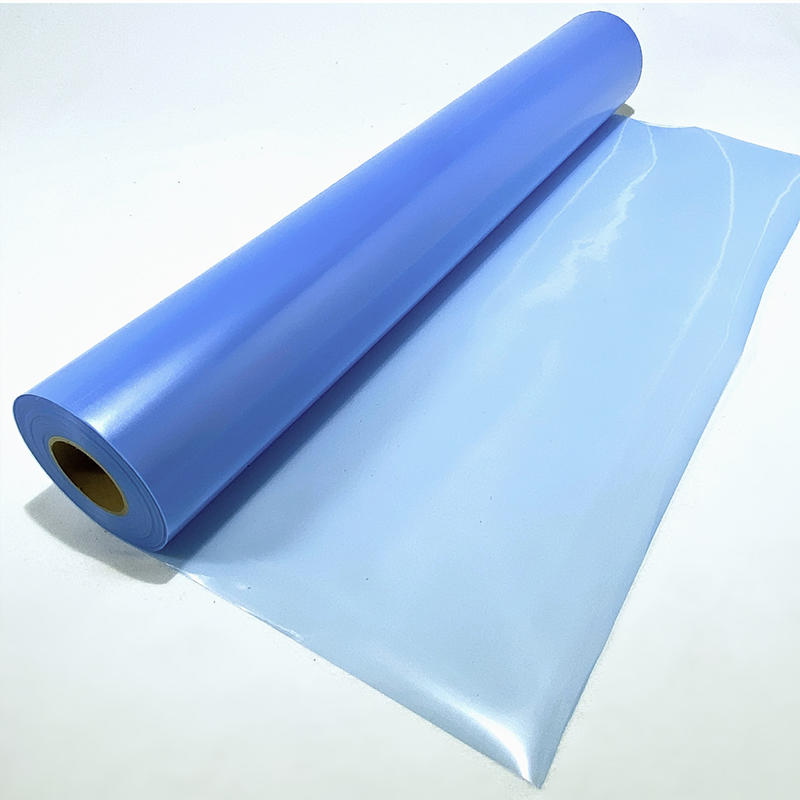
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) plain film, also known as PVC sheeting, is a versatile material used in various industries for its durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. PVC plain film can be classified based on several factors, including its composition, thickness, and application. Here are some common classifications of PVC plain film:
Composition:
a. Flexible PVC Film: This type of
PVC plain film is formulated with plasticizers to make it flexible and pliable. It is commonly used in applications that require bendability, such as in packaging, stationery, inflatable products, and protective covers.
b. Rigid PVC Film: Rigid PVC plain film does not contain plasticizers and is stiffer and less flexible compared to flexible PVC film. It is commonly used in applications that require rigidity and structural stability, such as in construction, signage, medical devices, and thermoforming.
Thickness:
a. Thin PVC Film: Thin PVC plain film typically has a thickness ranging from a few microns up to a few millimeters. It is used in applications that require a lightweight and thin material, such as in packaging, printing, laminating, and surface protection.
b. Thick PVC Film: Thick PVC plain film is generally thicker than thin film and can range from several millimeters to centimeters in thickness. It is used in applications that require a higher level of durability, strength, and impact resistance, such as in industrial applications, construction, and fabrication of rigid structures.
Application:
a. Packaging Film: PVC plain film is commonly used in the packaging industry for applications such as shrink wrap, blister packaging, vacuum forming, and clamshell packaging. It provides excellent clarity, protection, and tamper resistance to packaged goods.
b. Printing Film: PVC plain film is used as a printable material for various printing methods, including screen printing, digital printing, and offset printing. It provides a smooth and consistent surface for high-quality graphic reproduction.
c. Lamination Film: PVC plain film is used as a laminating material to protect and enhance the appearance of printed materials, such as posters, photographs, menus, and ID cards. It can be used as a top layer or as a middle layer in lamination processes.
d. Stationery and Office Supplies: PVC plain film is used in the production of stationery and office supplies, such as file folders, binders, document covers, report covers, and bookbinding materials. It provides durability, flexibility, and water resistance to these products.
e. Industrial Applications: PVC plain film finds applications in various industrial sectors, such as automotive, electrical, construction, and manufacturing. It is used for insulation, protective covers, gaskets, membranes, and other applications that require resistance to chemicals, oils, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures.
PVC plain film offers a wide range of possibilities and can be customized to meet specific requirements in terms of color, transparency, surface finish, and other properties. Its versatility makes it suitable for a diverse range of applications across different industries.
 English
English










 WeChat
WeChat WhatsApp
WhatsApp